Suspension abnormal noise accounts for a very large proportion of chassis abnormal noise, what kind of abnormal noise is there, and how should we repair it? Today I am here to teach you how to find the fault location based on the sound of the abnormal sound of the chassis.
1. The ball heads are worn or the ball head screws are loose

Fault description: When the vehicle bumps, the chassis makes a “cracking” sound.
Fault inspection: You can lift the vehicle and shake the tires to check the size of the gap, or use a crowbar to check the gap and looseness of each ball joint.
Solution: Tighten the bolts, replace the new connecting rod, connect the ball head, etc.
2. The rubber buffer rubber of the control arm is aging and damaged

Fault description: When the vehicle bumps, the chassis makes a “cracking” sound.
Fault inspection: Use a crowbar to pry each buffer rubber to check whether it is cracked or aged.
Solution: Replace with new swing arm buffer glue or new swing arm assembly.
3. The shock absorber is damaged by oil leakage
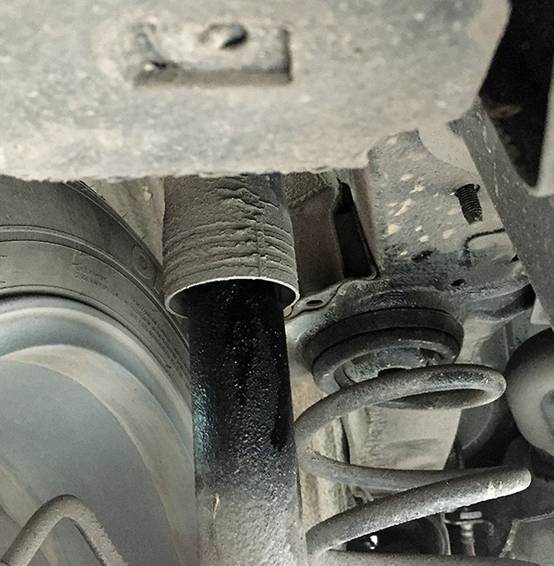

Fault description: There is a “click” or “creak” sound when bumps occur.
Fault inspection: Check the appearance of the shock absorber for signs of oil leakage, press the four corners of the car with your hands, check the bouncing of the body and whether there is any abnormal noise.
Solution: replace the new shock absorber.
4. Abnormal sound of top glue or plane bearing

Fault description: There will be a “dong dong” sound when passing the speed bump, and there will also be a “squeak” sound when turning the direction on the spot.
Fault inspection: You can listen to the sound by turning the direction on the spot or turning the car up.
Solution: Replace with a new top rubber or plane bearing, or add grease. Some noises are caused by loose screws on the vibration damper.
5. Abnormal sound from the rubber sleeve of the balance bar
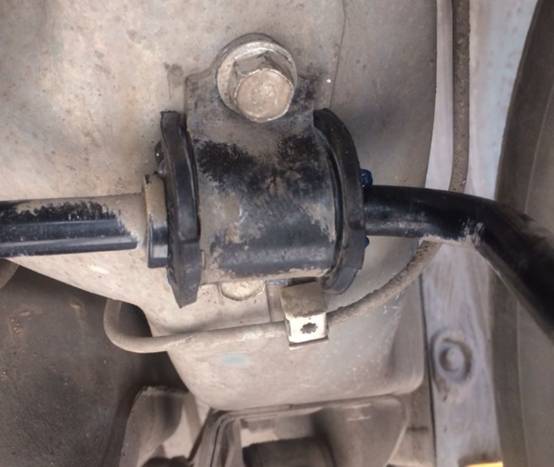

Fault description: There will be abnormal noises of “cracking” or “creaking” when driving and stepping on the brakes.
Fault inspection: check whether there are clean and worn parts on both sides of the rubber sleeve, and some are not easy to find, generally eliminated by replacement.
Solution: Replace the rubber sleeve of the balance bar with a new one.
6. The connection and fastening parts are loose
Fault description: There is a “click” abnormal sound when the bump occurs.
Fault inspection: Use a crowbar to pry to check whether each part is loose.
Solution: Tighten loose screws.
In order to make it easier for everyone to understand the structure of the chassis suspension system, you can see some basic introductions about the suspension system as follows.
1. Definition
Suspension is the general term for the device that transmits force between the frame (or load-bearing body) and the axle (or wheel) of a car.
2. Function
It transmits the force and moment between the wheel and the frame, and buffers the impact force transmitted from the uneven road to the frame or body, reducing the vibration caused by it, so as to ensure the smooth driving of the car.
3. Composition
The suspension is mainly composed of three parts: elastic elements, guiding devices and shock absorbers.
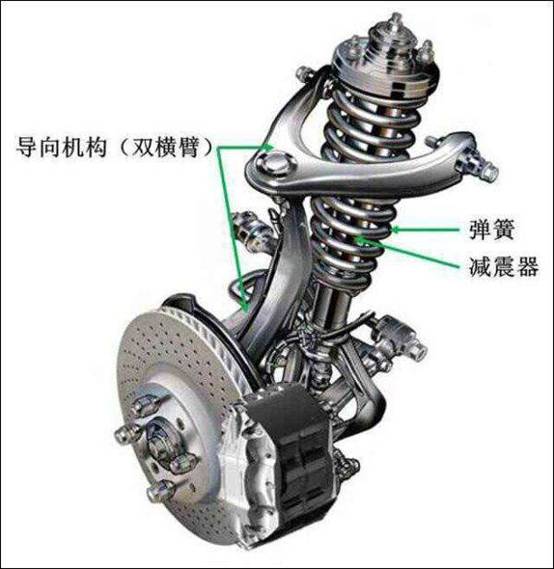
Elastic elements: made of materials with high elasticity, mainly to support vertical loads, ease and restrain vibration and impact caused by uneven road surfaces. For example, when the wheel is subjected to a large impact, the kinetic energy is converted into elastic potential energy and stored, and released when the wheel jumps down or returns to the original driving state.
Elastic elements mainly include leaf springs, coil springs, torsion bar springs, air springs and rubber springs.

Guide device: The function of the guide device is mainly to transmit force and moment, and also has a guiding role. During the running of the car, control the trajectory of the wheels.
Shock absorber: The shock absorber is the main component that generates damping force. Its function is to quickly attenuate the vibration of the car, improve the ride comfort of the car, and enhance the adhesion between the wheel and the ground.
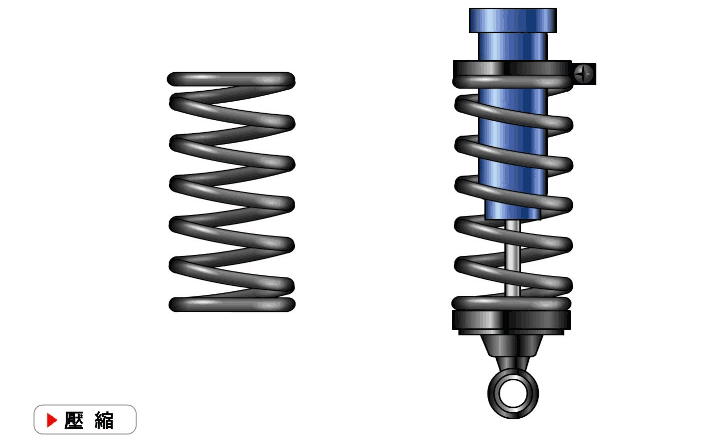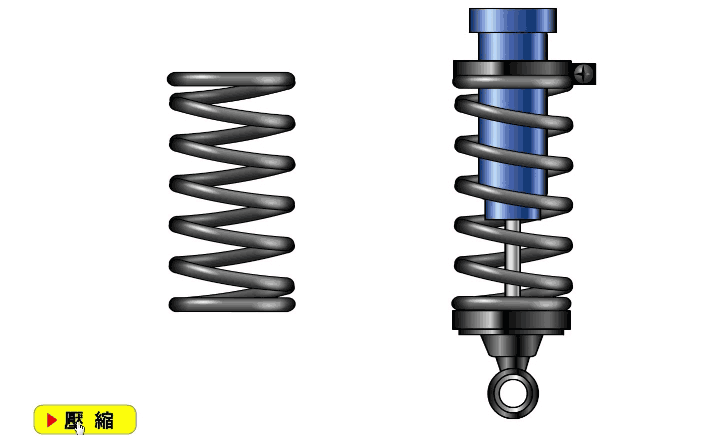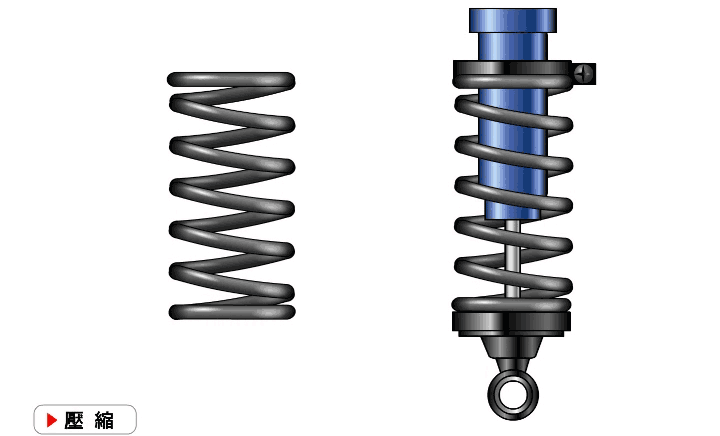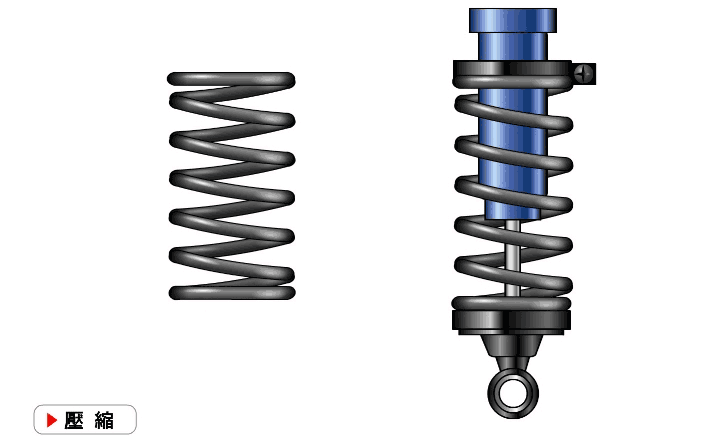
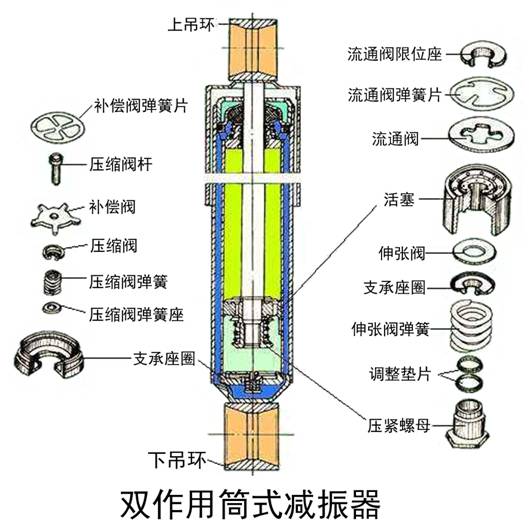
At present, the shock absorbers widely used in automobiles are mainly cylinder hydraulic shock absorbers, and their structures can be divided into three types: double cylinder type, single cylinder inflatable type and double cylinder inflatable type.
4. Classification of suspension
According to the basic form of its guiding device, it can be divided into two categories: non-independent suspension and independent suspension.
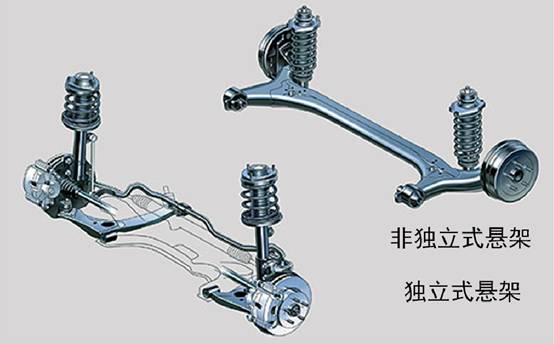
non-independent suspension
The wheels on both sides are connected by an integral axle, and the wheels together with the axle are suspended under the vehicle body through elastic suspensions. When one side of the wheel jumps, it will interfere with the other side of the wheel.
Advantages: simple structure, low cost, high strength, easy maintenance.
Disadvantages: poor comfort and handling stability.
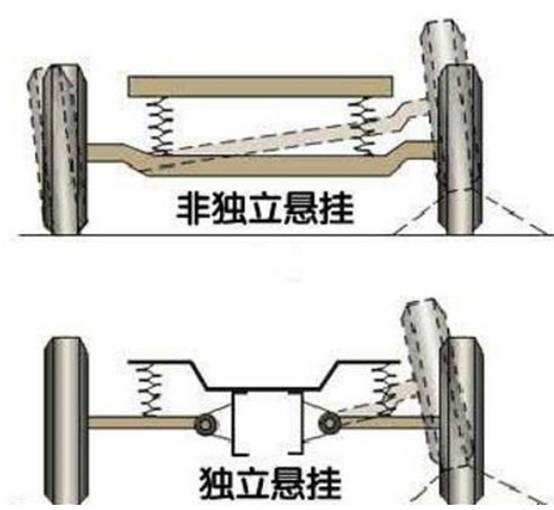
independent suspension
The wheels on each side are individually suspended from the frame or under the body by elastic suspensions. The left and right wheels dance independently without interfering with each other.
Advantages: light weight, reducing the impact on the body, improving the comfort and stability of the vehicle.
Disadvantages: complex structure, high cost, and inconvenient maintenance.
Most of today’s cars use independent suspensions, which can be divided into wishbone suspensions, trailing arm suspensions, multi-link suspensions, candle suspensions, and McPherson suspensions according to different structural forms.
A. Cross-arm type
Refers to the independent suspension in which the wheels swing in the transverse plane of the vehicle. It can be divided into single-arm type and double-arm type according to the number of cross-arms.
single wishbone
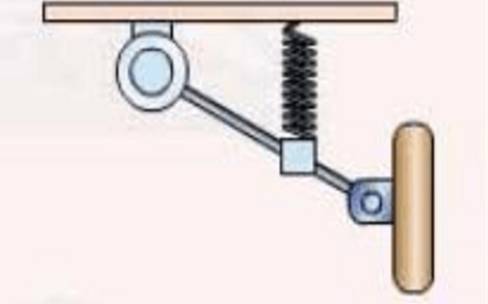
Advantages: simple structure, high roll center, and strong anti-roll capability.
Disadvantages: tire wear is large, not suitable for high-speed driving.
double wishbone
According to whether the upper and lower cross arms are equal in length, it can be divided into equal length double wishbone type and unequal length double wishbone type.
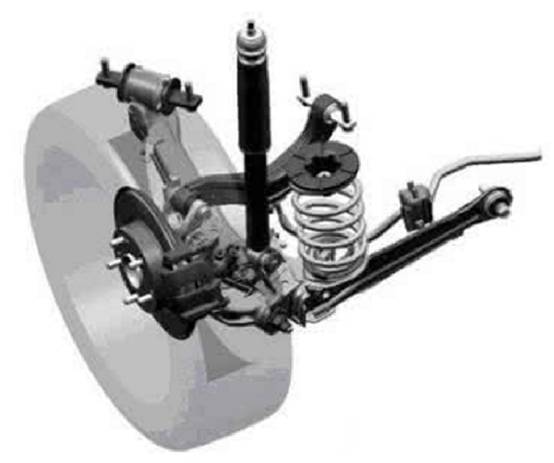

The equal-length double-wishbone suspension can keep the kingpin inclination constant when the wheel jumps up and down, but the wheelbase changes greatly and the tires wear seriously.
The unequal-length double-wishbone suspension has a large lateral stiffness, which can make the changes of the wheel base and front wheel alignment parameters within a limited position, so as to ensure that the car has good driving stability.
The upper and lower arms of the double wishbone cannot play the role of longitudinal guidance, and an additional tie rod guide is required.
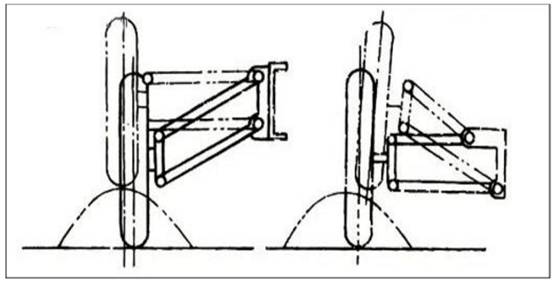
double wishbone
It is changed from the double wishbone type, and replaces the single arm of the double wishbone type with an A-shaped or V-shaped structure.
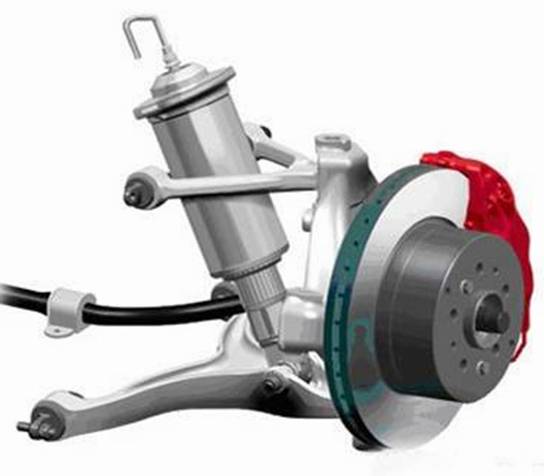

Advantages: large lateral stiffness, good directional stability, excellent roll resistance, and good grip.
Disadvantages: high manufacturing cost, complicated setting of positioning parameters, large horizontal installation space.
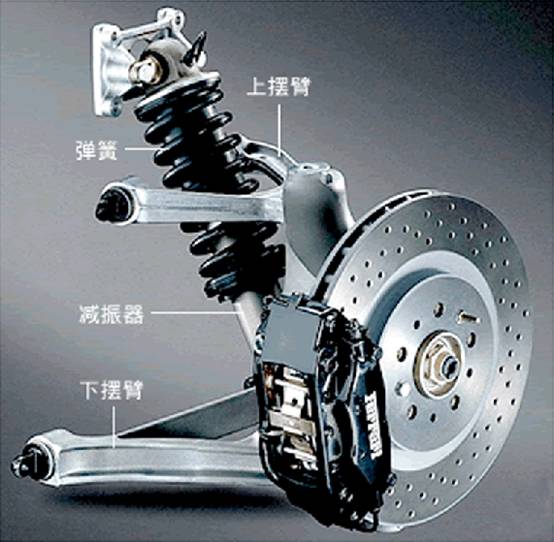
B. Longitudinal arm type
It refers to the suspension in which the wheels swing in the longitudinal plane of the car. According to the number of trailing arms, it can be divided into single trailing arm type and double trailing arm type.
single trailing arm
When the wheel jumps, the trailing arm swings around the axis of the bushing, causing the torsion bar spring to twist and deform to ease the impact of the uneven road surface. Therefore, when the wheel moves up and down, the caster angle will change greatly.
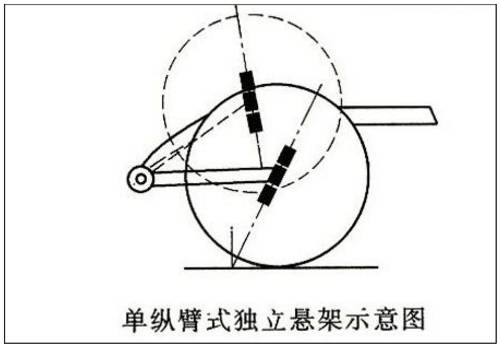
double trailing arm
The double trailing arm suspension has two trailing arms, and the lengths of the two trailing arms are generally made equal to form a parallel four-bar linkage. In this way, when the wheels run up and down, the caster angle remains unchanged, so this form of suspension can be used as a steering suspension.
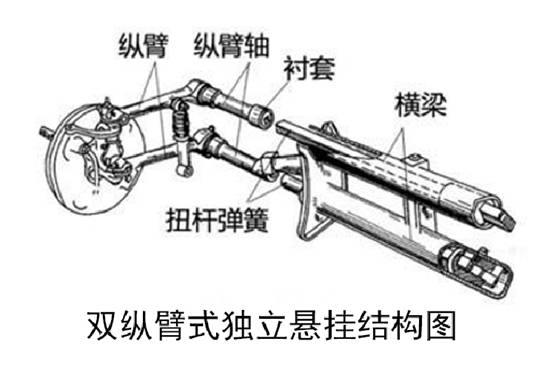
C, multi-link
A suspension consisting of multiple (3-5) rods combined to control the position of the wheels.

Advantages: strong comfort and handling stability.
Disadvantages: relatively complex, high cost, and large space occupation.
D. Candlestick
The main pin of the candle suspension is fixed on the vehicle frame through the upper and lower support plates, and the steering knuckle is small and exquisite. The wheels move up and down along a kingpin axis that is rigidly fixed to the frame.
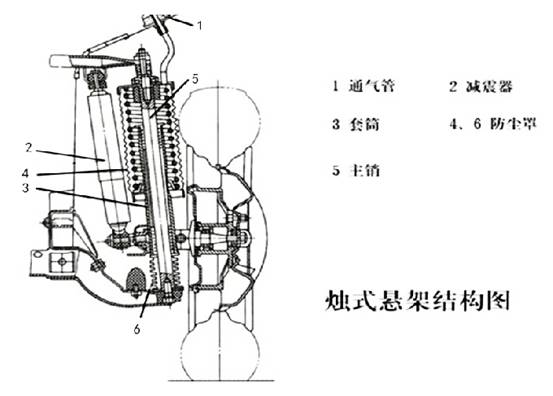
Advantages: Steering maneuverability and driving stability are strong.
Disadvantages: The main pin is easy to wear and tear.
E. McPherson
Consists of coil springs, shock absorbers and triangular (A-shaped) lower arms. It is the most widely used car front suspension at present.
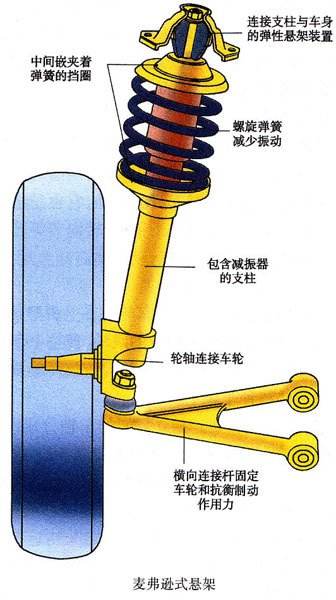
Advantages: simple structure, small size and light weight.
Disadvantages: Since the shock absorber and the coil spring both support and buffer the up and down shaking of the vehicle, there is not enough support for the lateral force, and it is easy to roll, and there is obvious nodding phenomenon when braking.
5. Adjustable suspension system
A. Air adjustable suspension
A suspension method that uses an air compressor to form compressed air and adjusts the ground clearance of the car chassis through the compressed air.
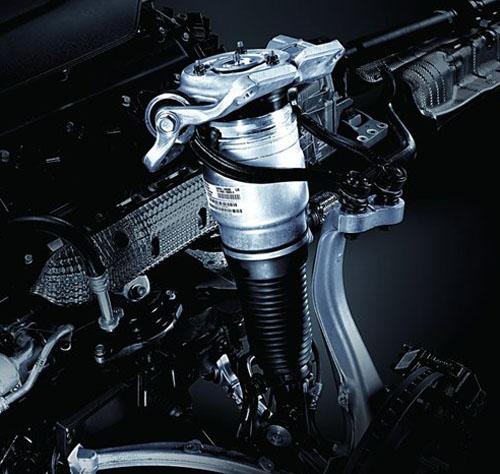

B. Hydraulic adjustable suspension
Adjust the ground clearance of the car chassis by increasing or decreasing the hydraulic oil to realize the height change of the vehicle body.

C. Electromagnetic adjustable suspension
Electromagnetic response is used to realize the height change of the car chassis. It can respond to road conditions within 1 millisecond, suppress vibrations, and keep the body stable.
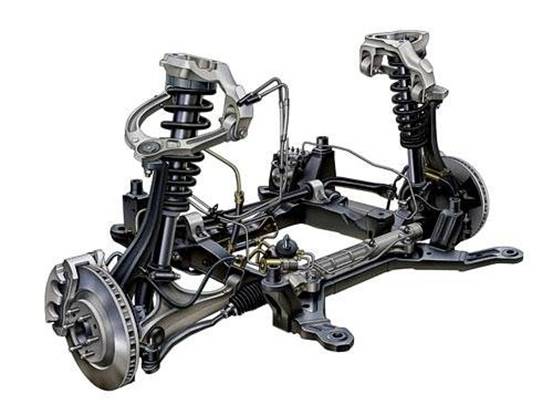

6. Other failures of the suspension system
A. Body tilt
a. Vibration damping oil leakage damage
b. The damping spring is broken
c. Damaged adjustable suspension
d. Improper adjustment of adjustable vibration reduction
B. Abnormal tire wear
It is mainly caused by incorrect four-wheel alignment parameters or failure to do four-wheel alignment after replacing new parts.
Source of pictures and texts: This article is compiled and edited by “Auto Repair Collection – Guyun”.