1. Definition
Suspension is the general term for all force transmission connection devices between the vehicle frame (or load-bearing body) and the axle (or wheel), and its function is to transmit the force and force acting between the wheel and the frame Torsion, and buffer the impact force transmitted to the frame or body from the uneven road, and reduce the vibration caused by it, so as to ensure that the car can run smoothly.
2. Composition The
suspension is composed of three parts: elastic elements, guiding devices and shock absorbers.
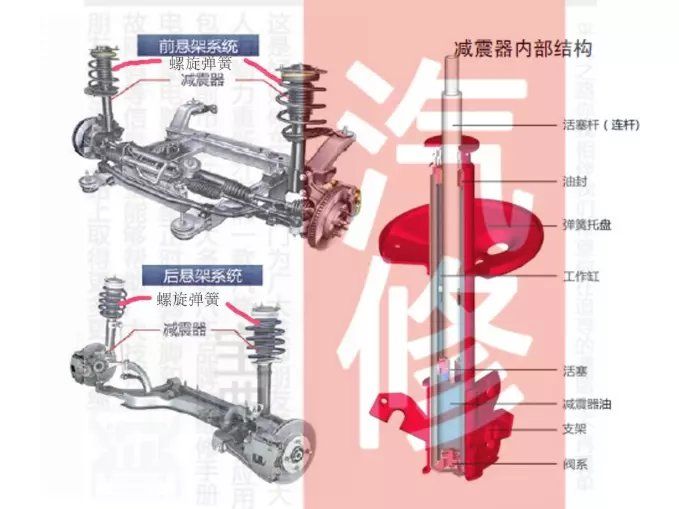
1. Elastic element: supports vertical load, moderates and restrains vibration and impact caused by uneven road surface. Elastic elements mainly include leaf springs, coil springs, torsion bar springs, air springs and rubber springs. Parts made of materials with high elasticity, when the wheel is subjected to a large impact, the kinetic energy is converted into elastic potential energy and stored, and released when the wheel jumps down or returns to its original driving state.
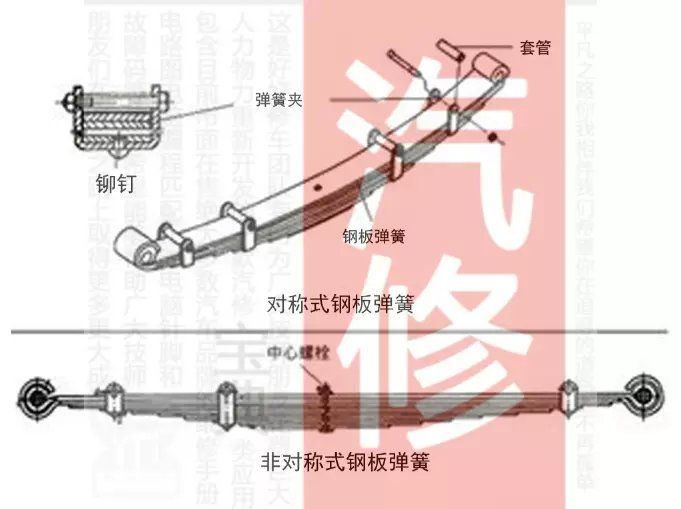




2. Guide device: The function of the guide mechanism is to transmit force and moment, and also play a guiding role. During the driving process of the car, the trajectory of the wheels can be controlled.
3. Shock absorber: The shock absorber is the main component that generates damping force, and its function is to quickly attenuate the vibration of the car. Improve the ride comfort of the car and enhance the adhesion between the wheels and the ground. In addition, the shock absorber can reduce the dynamic load of the body part and prolong the service life of the car. The shock absorbers currently used in automobiles are mainly cylinder-type hydraulic shock absorbers, and their structures can be divided into three types: double-tube type, single-tube inflatable type and double-tube inflatable type.
3. Classification of Suspension
According to the basic form of its guiding device, it can be divided into two categories: non-independent suspension and independent suspension.
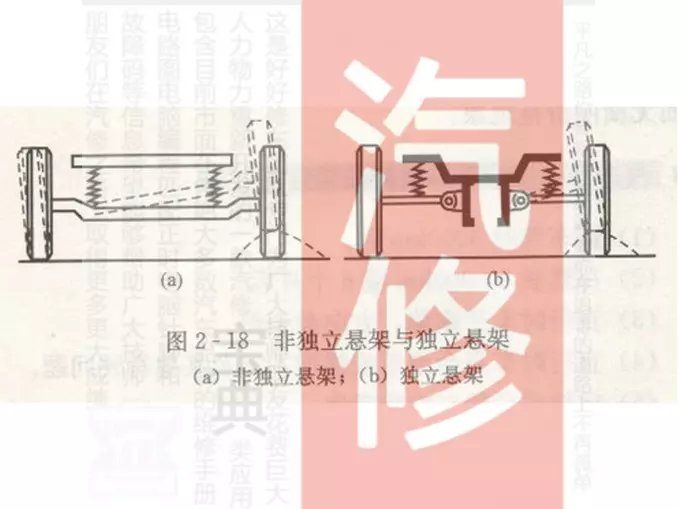
1. Non
-independent suspension The structural feature of non-independent suspension is that the wheels on both sides are connected by an integral axle, and the wheels together with the axle are suspended under the frame or vehicle body through elastic suspension. The non-independent suspension has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high strength, easy maintenance, and small changes in front wheel alignment during driving. However, due to its poor comfort and handling stability, it is basically no longer used in modern cars, and it is mostly used in trucks and buses. I won’t introduce too much here.
2. Independent suspension
Independent suspension is that the wheels on each side are individually suspended from the frame or under the vehicle body through elastic suspensions. Its advantages are: light weight, reducing the impact on the body, and improving the ground adhesion of the wheels; soft springs with small stiffness can be used to improve the comfort of the car; the position of the engine can be lowered, and the center of gravity of the car can also be lowered, thereby Improve the driving stability of the car; the left and right wheels jump independently and are independent of each other, which can reduce the tilt and vibration of the car body. However, the independent suspension has the disadvantages of complex structure, high cost and inconvenient maintenance. Most modern cars use independent suspensions. According to different structural forms, independent suspensions can be divided into wishbone suspensions, trailing arm suspensions, multi-link suspensions, candle suspensions, and MacPherson suspensions.
A. Cross-arm suspension
Cross-arm suspension refers to the independent suspension in which the wheels swing in the transverse plane of the vehicle. It is divided into double-arm suspension and single-arm suspension according to the number of cross-arms.
The single wishbone type has the advantages of simple structure, high roll center and strong anti-roll capability. However, with the increase of the speed of modern cars, the excessively high roll center will cause a large change in the wheel track when the wheels jump, and the tire wear will increase. Moreover, the vertical force transfer of the left and right wheels will be too large during sharp turns, resulting in increased camber of the rear wheels. The cornering stiffness of the rear wheel is reduced, resulting in severe conditions of high-speed tail drift. The single-wishbone independent suspension is mostly used in the rear suspension, but because it cannot meet the requirements of high-speed driving, it is not used much at present.
Double-wishbone independent suspension is divided into equal-length double-wishbone suspension and unequal-length double-wishbone suspension according to whether the upper and lower cross-arms are equal in length. The equal-length double-wishbone suspension can keep the kingpin inclination constant when the wheel jumps up and down, but the wheelbase changes greatly (similar to the single-wishbone suspension), which causes serious tire wear and tear, and is rarely used now. For the unequal-length double-wishbone suspension, as long as the length of the upper and lower wishbone is properly selected and optimized, and through reasonable arrangement, the changes of the wheelbase and front wheel alignment parameters can be kept within acceptable limits, ensuring that the vehicle Has good driving stability. At present, the unequal-length double-wishbone suspension has been widely used in the front and rear suspensions of cars, and the rear wheels of some sports cars and racing cars also use this suspension structure.

B. Trailing arm suspension
Trailing arm independent suspension refers to the suspension structure in which the wheels swing in the longitudinal plane of the vehicle, and it is divided into two types: single trailing arm type and double trailing arm type. The single trailing arm suspension will cause a large change in the caster angle when the wheel jumps up and down, so the single trailing arm suspension is not used on the steering wheel. The two swing arms of the double trailing arm suspension are generally made into equal lengths to form a parallel four-bar structure. In this way, when the wheels jump up and down, the caster angle of the kingpin remains constant. Double trailing arm suspension is mostly used on steering wheels.
C. Multi-link suspension
The multi-link suspension is a suspension in which (3-5) rods are combined to control the position change of the wheel. The multi-link type can make the wheels swing around the axis at a certain angle with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. The advantages of cross-arm suspension and trailing-arm suspension are obtained to different degrees, and different performance requirements can be met. The main advantages of the multi-link suspension are: the change of the wheel base and the toe in is very small when the wheels jump, and the car can turn smoothly according to the driver’s intention in the driving and braking states. Occasionally, there is a phenomenon of shaft swing.
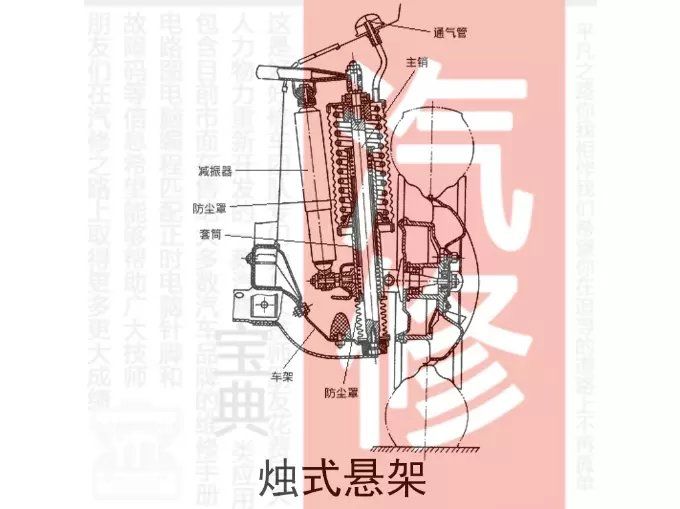
D. Candle Suspension
The Candle Suspension is a construction in which the wheel moves up and down along the axis of a king pin rigidly fixed to the frame. The advantage of the candle suspension is: when the suspension is deformed, the positioning angle of the kingpin will not change, only the wheelbase and wheelbase will change slightly, so it is especially beneficial to the steering stability and driving stability of the car. But the candle suspension has a big disadvantage: that is, the lateral force when the car is running will all be borne by the kingpin sleeved on the kingpin sleeve, resulting in increased frictional resistance between the sleeve and the kingpin, and serious wear and tear. Candle suspension is not used much now.
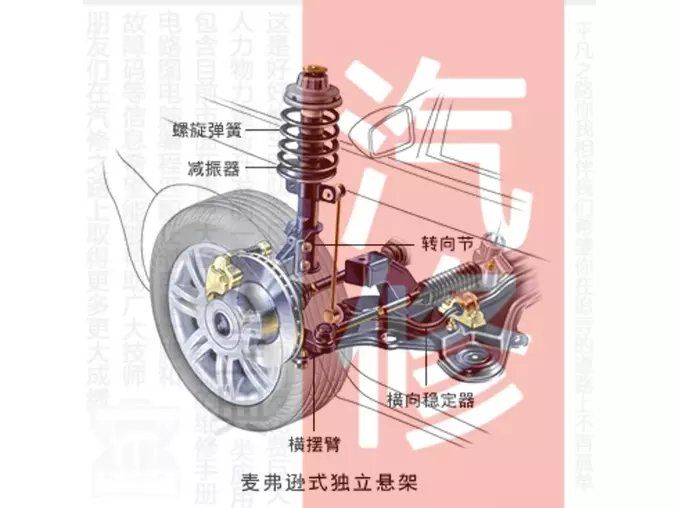
E. McPherson
suspension The wheel of the MacPherson suspension is also a suspension that slides along the kingpin, but it is not exactly the same as the candle suspension. Its kingpin can swing, and the McPherson suspension The rack is a combination of swing arm and candle suspension. Compared with the double-wishbone suspension, the advantages of the MacPherson suspension are: compact structure, small changes in the alignment parameters of the front wheels when the wheels jump, and good handling stability. The arrangement of the engine and the steering system brings convenience; compared with the candle suspension, the lateral force received by its strut has been greatly improved.
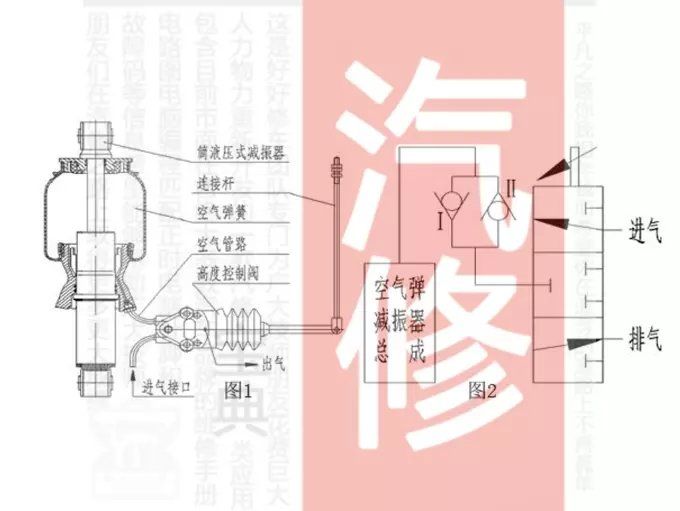
4. Air suspension
A high-quality SUV should not only have the comfort of a car, but also take into account the passing performance of an off-road vehicle. The air suspension system is the best choice to achieve this goal. According to different road conditions and the signal of the distance sensor, The trip computer will judge the height change of the vehicle body, and then control the air compressor and exhaust valve to automatically compress or extend the spring, thereby reducing or increasing the ground clearance of the chassis to increase the stability of the vehicle body at high speeds or the passability of complex road conditions.
Source of pictures and texts: This article was originally created by Auto Repair Collection – Guyun.