The outflow of rural labor force has led to the abandonment of farmland and the problem of no agricultural successors. In this context, Japan integrates agricultural production and art processing, and uses rural scenery to meet people’s recreational needs, as an effective way to upgrade industries, increase value, and increase residents’ income.
Business Thinking in Japanese Agriculture
The success of Japanese leisure agriculture is closely related to its business thinking. The agricultural business thinking of Japanese farmers is mainly manifested in three aspects: product quality, ecological closed loop, and industrial premium.
1 Product quality: Lean dead knock single product
An important goal of Japanese farmers in production is the pursuit of quality. Taking rice as an example, the yield per mu is generally only 300-400 kilograms, but the rice produced is superior both in appearance and taste. Therefore, Japanese agricultural products not only sell well, but also have good prices.
At the same time, the professional division of labor in Japanese agricultural production is very clear. Each region has its own industrial characteristics, and each farmer has its leading product. Complementary advantages and interdependence form the overall framework of Japan’s agricultural economy.
Generally speaking, Japanese farmers are all professional households. Those who grow strawberries grow strawberries, those who grow tomatoes grow tomatoes, and those who grow flowers grow flowers. Generally, farmers only produce 1 to 2 varieties throughout the year, no more than 3 varieties at most, and almost all of the products produced are commodities, and the commodity rate of agricultural products is extremely high.
The attitude of sticking to single products wins the favor of consumers or the market.
2 Ecological closed loop: looking for premium space
The Japanese are very good at doing business, and at the same time they have perfect considerations for one thing. This may be a way of thinking instilled in them since childhood, and a “closed-loop” development model was adopted for them very early on agricultural issues.
For any business model or any service, as long as it can achieve closed-loop development, it can expand the profit space.
They form a closed-loop industrial link unique to agriculture through production, processing, sales, and service, thereby increasing the driving force for profit and development.
3 Industry premium
“Six industries” was first proposed by Japanese scholar Imamura Naramitsu in the 1990s. At that time, Japan was facing the problems of lack of agricultural successors and rural decline.
In order to stimulate the vitality of agricultural development, we began to promote the extension of agricultural production to the secondary and tertiary industries, forming a complete industrial chain integrating production, processing, sales, and service, thereby increasing farmers’ income and enhancing the vitality of agricultural development.
For example, in Malu Village, the village head and the head of the agricultural association led the whole village’s “lumberjacks” to transform into “six industrial entrepreneurs.” Plant organic pomelo, and then organize villagers to further process the pomelo to make pomelo jam, pomelo drink, pomelo soup, etc.
At the same time, a hot spring homestay and a direct sale of agricultural and forestry products will be built to attract consumers from big cities such as Tokyo and Osaka to visit Malu Village. By the end of 2016, more than 10,000 people around the world have become special residents of Malu Village. It receives more than 300 groups a year to experience and study, and sells more than 10 million items, with annual sales reaching 200 million yuan.

Characteristics of Japanese Leisure Agriculture
There are two most notable characteristics of Japanese leisure agriculture: one is creative agriculture, and the other is agricultural product packaging.
1 Creative Agriculture
Rice field painting is the core idea of Japanese agriculture. Inakadate Village is the originator of Japanese rice field painting. Inspired by the crop circle, villagers in the village began to make rice field paintings in 1993 in order to revitalize the local economy and develop tourism resources. The themes are different every year, covering a wide range of topics both inside and outside of Japan, including the famous ancient Japanese generals, Mona Lisa, Napoleon, and even anime images such as Doraemon.
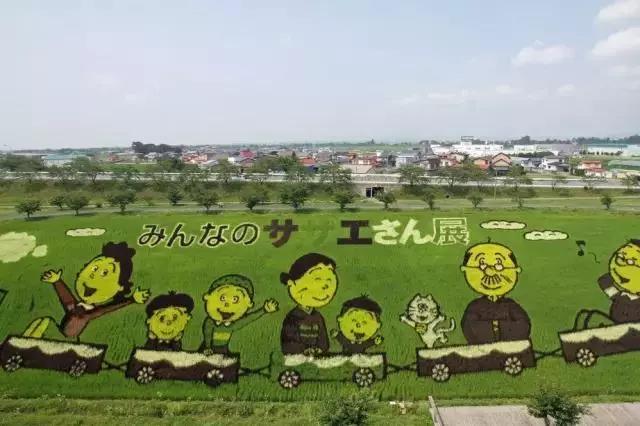

This kind of rice field art can be divided into two viewing methods according to different planting methods: one is looking down. Visitors to watch take a crane or a helicopter, but this method is a bit embarrassing for tourists with fear of heights; the second method is called “far and near method”. The so-called “far and near method” is a method of planting rice field paintings from near to far designed to facilitate tourists to clearly see the huge scrolls in the rice fields on the viewing platform on the ground.
Today, more than 200,000 people visit Tiansheguan Village every year. This is really the “tourism” produced by farming. There are even some big companies coming to their door, hoping to use the rice field paintings of farmers to make “advertisements” for them.
2 Agricultural product packaging
The reason why Japanese agriculture is “world-renowned” is not only the quality, but also the packaging. The packaging of Japanese agricultural products can be described as stunning.
Japanese agricultural and sideline products are of high quality. Whether it is a popular product or a new and excellent variety, they are all bright in color and uniform in size, which is pleasing to the eye.
In the market, all agricultural products to be sold are carefully sorted and packaged, not sold in bulk, and not sold with mud or dead leaves. The packaging boxes of agricultural products are printed with the name of the product, place of origin, and the name of the producer.
At the same time, cabbage is sold in whole boxes, one piece, or cut into half or quarter pieces, all of which are sealed and packaged with plastic paper. If the cut cabbage cannot be sold that day, it will be thrown away at night. There are 10 or 5 boxes of peppers, all of which are neatly arranged on the shelves. The beautiful appearance and delicious taste of radish, melon, strawberry, cherry and tomato all leave a deep impression on people.
In addition to the internal arrangement and packaging, there is also the appearance and packaging design, which has reached the stage of stunning metamorphosis.
Because Japan is one of the countries that pay attention to packaging most in the world. They extract the essence of Zen in Japanese culture, and then convey some natural, simple, and lovely elements, and the final design is simple but unique. , Deep ultimate taste.

The Management Way of Leisure Agriculture in Japan
Why can Japan’s leisure agriculture develop so well? This is closely related to its way of doing business.
1 Industrialization
Through land transfer, Japan has formed large-scale, industrialized planting and breeding areas around cities, incorporating elements of leisure and entertainment, and creating pastoral scenery to attract audiences.
At the same time, extend the industrial chain on the basis of agriculture, increase service functions, rely on agriculture, and integrate three or more related industries such as industry, tourism, creativity, research and development, commerce, storage and transportation, real estate, entertainment, exhibitions, and expos. While carrying out agricultural production and industrial management, it displays agricultural culture and rural life, thus forming a multi-functional, complex and innovative industrial complex.
2 Various marketing activities
Some people say that leisure farms in Japan are like holy places for festivals. It can be seen from this that Japanese leisure farms are very fond of “activities”, and this is the most common and popular marketing method for Japanese leisure agriculture.
Leisure agriculture is similar to supermarkets. In order to attract customers, supermarkets and shopping malls often carry out promotional activities, while farms need to organize more agricultural-related cultural activities to attract tourists and increase the popularity of their farms.
3 IP creation
Farm IP takes leisure agriculture as the core, and builds a comprehensive brand around this core to build the brand culture of the farm, which is a big IP.
The biggest feature of Japanese leisure farms is that they pay attention to the creation of the farm’s own IP. Once this IP is successfully created, it will bring a large number of hardcore fans to the farm. Whether it’s visiting or selling your farm’s produce, it will be easier later.
4 User relationship establishment
Japanese leisure agriculture attaches great importance to the establishment of user relationships. They will create leisure farms with their own characteristics according to the needs of users. Their main advantage is to establish a relationship of mutual trust between producers and users.
At the same time, farmers often invite users to come to the farm to experience or participate in entertainment activities, so that users can truly experience the difference of the farm. After continuous communication and interaction, the user’s trust and loyalty to the farm can be improved.
5 Brand building
Japanese leisure agriculture pays attention to brand building, mainly relying on user satisfaction to promote it. At the same time, relying on rural cultural resources and agricultural nature, we will create a well-known brand of leisure agriculture.
The brand concept of leisure agriculture is based on “integrity, low carbon, environmental protection, and ecology”. In this regard, Japan’s leisure agriculture focuses on the harmonious development of man and nature, and pays attention to environmental protection. The construction of infrastructure is also “different from place to place”, and the utilization rate of agricultural resources is optimal.

Reference and Enlightenment
1 Strengthen resource integration
Japan’s leisure agriculture is mostly based on the use of local agricultural resources, with a certain aspect as the main line, such as flower planting, supplemented by rice, breeding, and agricultural product processing, forming a relatively complete and diverse theme park for users to visit or It is experience, not just creating a certain feature, ignoring the advantages of other resources.
2 Pay attention to the protection of agricultural resources
Japan has a small land area, so the Japanese pay great attention to land protection. Protecting land resources and achieving sustainable development are their primary considerations in creating leisure agriculture.
Japan attaches great importance to resource protection and has achieved great results. In terms of leisure agriculture, although Japan will build infrastructure and some tourist attractions to protect the rights and interests of tourists, but in this regard, Japan will base on local conditions. Under the condition of being destroyed, complete the above work.
3 Based on localization
Rural Japan pays special attention to excavating and creating rural culture. The local cultural heritage and non-cultural heritage are carefully preserved, and then integrated with modern design concepts, which not only reflects the unique charm, but also injects the original culture into the leisure agriculture. In the process of brand building, localized products have been born.
The development of leisure agriculture is to adapt measures to local conditions, highlight local characteristics, make use of local characteristics such as regional natural resources and traditional culture, reasonably explore and develop green tourism products, and carry out scientific agricultural planning. The construction of scenic spots should retain their original rural and rural characteristics.
The outflow of rural labor force has led to the abandonment of farmland and the problem of no agricultural successors. In this context, Japan integrates agricultural production and art processing, and uses rural scenery to meet people’s recreational needs, as an effective way to upgrade industries, increase value, and increase residents’ income.
Source: Agricultural and Military Academy