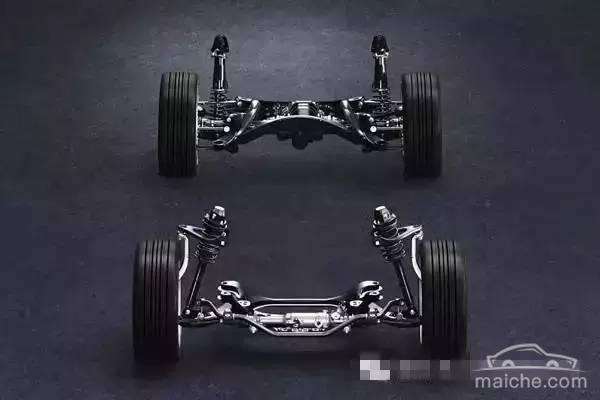
There are many types of SUVs on the market today with prices ranging from 250,000 to 400,000. For example, Toyota Land Cruiser has the lowest configuration, Toyota domestic Prado 2.7L, Land Rover Freelander 2, Volvo XC60, Audi Q5, Volkswagen Tiguan, Mercedes-Benz GLK, Mercedes-Benz GLA, BMW X1, Subaru Outback and so on. Each advertises its own powerful full-time/timely four-wheel drive system. But when you choose a car, do you know the characteristics of each four-wheel drive system, and which characteristics do you really want?
Today, let’s take a look at the basic principles and composition of the mainstream SUV four-wheel drive technology in the range of 250,000 to 400,000. I hope it can help you make better plans for buying a car. You may not be particularly concerned about some technical details, so I would like to remind you to pay special attention to which models have a mechanical solution for the center differential and which ones have an electronic solution. The mechanical solution is stable and reliable but the cost is high. The electronic solution is small and flexible but not stable enough to work for a long time. It is also important to look at which models are equipped with rear axle differential locks or limited slip differentials. If you are a little confused when you see various professional terms, such as what is a differential and a differential lock, then please read down slowly and explain it to you step by step.
If you played with a mini four-wheel drive model car when you were young, you may remember that its internal structure is to connect the front axle and the rear axle through a connecting rod with gears, so that the rotation speed of the four wheels is the same. So why doesn’t the current four-wheel drive SUV adopt such a structure? The problem is the steering system. Because the mini four-wheel drive model car only needs to walk along the track of the track without considering the steering problem, the speed of its four wheels can be the same. But when the car needs to turn when driving on the road, the speed of the wheels on the left and right sides is different. why? Turning a vehicle is similar to making a circular motion. According to the law of circumference, the circumference of a circle is equal to 2π times the radius. For example, when turning left, the radius of the left wheel near the center of curvature is small, and the circle drawn is also small. The principle of the right wheel is that the radius of the center of curvature is large, and the circle drawn is also large. Therefore, a transmission shaft cannot be directly used for hard link between the left and right wheels. In order to allow the car to still move forward when turning, the car is equipped with a device called a differential. The differential allows power to be transmitted at different wheel speeds. The principle is simply to add a set of relatively rotating pinion gears between the left and right transmission shafts. When the left and right wheels rotate at the same speed, the pinion is at rest, and the torque obtained by the wheels on both sides is the same. When there is a speed difference between the left and right wheels, the pinion gear starts to rotate, delivering more torque to the side of the wheel with a lower speed.
Differential
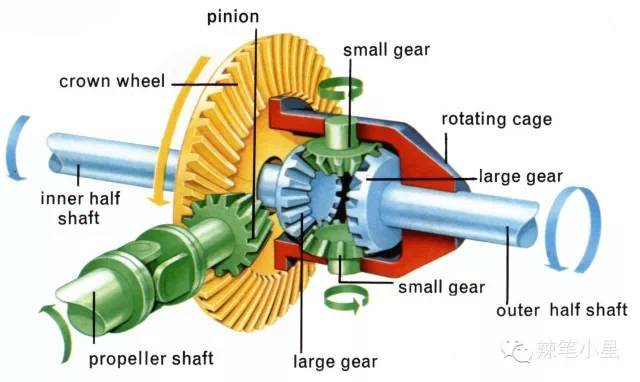
In order to allow a certain wheel speed difference between the left and right wheels when the vehicle is turning, the front and rear axles of the vehicle are equipped with differentials, which are respectively the front axle differential and the rear axle differential. Models equipped with a four-wheel drive system need to distribute power between the front and rear axles, so a central differential is added to the drive shaft in the middle. The center differential and transfer case work together to distribute power to the front and rear axles of the vehicle. The transfer case (Transfer Case), as the name suggests, is used to distribute power, which is similar to the gear structure connecting the front and rear axles inside the mini four-wheel drive model car. The center differential and transfer case are sometimes combined in an automatic transmission.
It can be said that all the challenges to the four-wheel drive system come from the aforementioned differential. Because the differential allows a speed difference between the wheels. However, when the vehicle is on off-road conditions or icy and snowy conditions, it is very likely that one or more wheels will lose grip and slip. At this time, due to the existence of the differential, the slipping wheels lose a lot of power due to the rapid rotation because there is no friction. And the side wheel that has frictional force is almost static and can not get power. You may have doubts here. Didn’t you say that the differential will send more torque to the wheels with low speed? This is indeed the case, but there is a prerequisite for this function, that is, the speed difference between the wheels should not be too large. Therefore, when slipping, there will be a loss of power from the wheel on the side that has no friction and is spinning rapidly as mentioned above.
So let’s take a look at how each four-wheel drive system meets this challenge.
First of all, the easiest way is of course to manually rigidly connect the rotating shafts at both ends of the differential by mechanical means when off-roading is required. After locking, the speed difference will no longer exist. This is the differential lock, or also known as the jaw differential lock or part-time four-wheel drive system. For example, the Toyota Land Cruiser currently on the market is equipped with a central differential lock button and a rear axle differential lock button. The domestically produced Toyota Prado 2.7L version is equipped with a central differential lock button. For professional off-road vehicles with higher prices, such as Mercedes-Benz G series and Jeep Wrangler, as shown in the figure below, they are equipped with front axle differential lock, central differential lock button and rear axle differential lock button at the same time. What needs to be reminded here is that after the front differential lock is activated, steering cannot be performed on paved roads (roads). The reason is that after the differential lock is activated, the speed difference caused by the steering of the left and right wheels is no longer allowed. Otherwise, an accident may occur or the vehicle may be damaged.
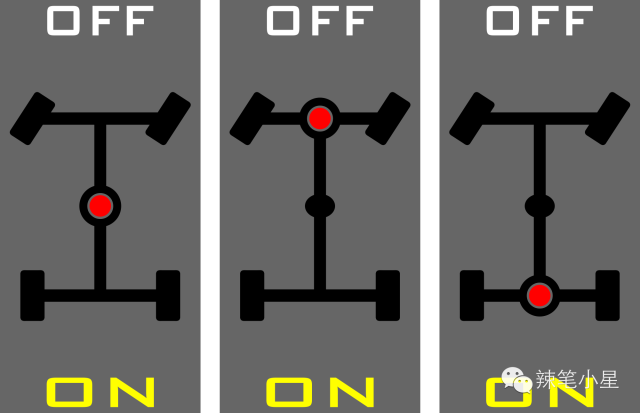
Then everyone has also seen that differential lock is the easiest way, but its problems are also obvious. It just needs to be turned on manually. More suitable for professional off-road conditions. So is there a way to fully automate the switching of the four-wheel drive mode during daily driving? That is the full-time/timely four-wheel drive system introduced later. Here we first focus on the central differential of the full-time/timely four-wheel drive system. Because it is the key to the vehicle to achieve four-wheel drive. is how it distributes power between the front and rear axles.
The central differential mainly includes the following types:
-
open center differential
-
Torsen Differential
-
Viscous Coupling Differential
-
Multi-plate Clutch Differential
Having said so many technical terms is not conducive to everyone’s quick understanding of the four-wheel drive system. Going back to the previous article, please follow me to take a look at the two camps of the mechanical school and the electronic school of the central differential. Let’s take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of different types of central differentials.
The first is the mechanical school. The so-called mechanical school means that the torque distribution of the central differential does not require electronic control, and the torque can be adjusted on demand directly through mechanical design.
The central differential based on the mechanical solution is characterized by :
-
Adjustments are made when torque changes, without significant changes in wheel speed
-
No electronic control system is required, so it can work in harsh environments such as sandy land and wading water. reliable and stable
-
The torque is determined according to the road conditions, and cannot be actively adjusted and distributed
-
Larger size and higher cost
-
If the rear wheels touch the ground while towing, the front wheels will spin along with it, which may damage the four-wheel drive system
Among the four types of central differentials mentioned above, the open differential is the most traditional differential that does not have the ability to lock and can only cooperate with the differential lock. It is neither mechanical nor electronic, so it is not listed. The remaining Torsen torque-sensing transmissions and viscous coupling differentials are mechanical. Among them, the Torsen torque-sensing transmission is the mainstream technology among the mechanical schools. Representative models include Toyota Land Cruiser with the lowest configuration, Toyota’s domestic Prado 2.7L and Audi Q5. The higher-priced Range Rover and Audi’s S4 or A6 Quattro all use this type of center differential.
Briefly introduce the principle of Torsen torque induction transmission. As shown in the figure below, the core of the Torsen torque induction transmission is two sets of spur gears (Spur Gear) and worm gears (Worm Gear) linked between the two output shafts. Through mechanical design, the output shaft can drive the worm gear to rotate, but the worm gear cannot drive the output shaft to rotate. The linkage between the two output half shafts is thus established via the worm gear. The rotational speeds of the two output half shafts must not differ greatly. When the speed increases due to slipping on one side, it will be locked by the frictional side on the other side. More torque is transferred to the friction side (up to 70% of torque).
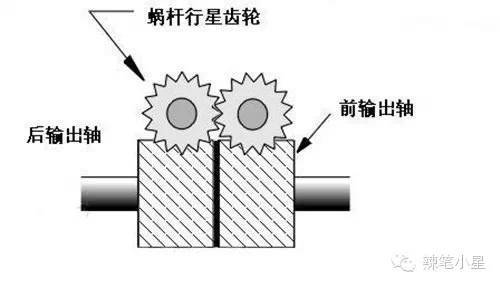
For example, the Torsen torque induction transmission used in the Audi Quattro full-time four-wheel drive system shown in the figure below (applied in the Audi A4 and Q5 Quattro four-wheel drive models):
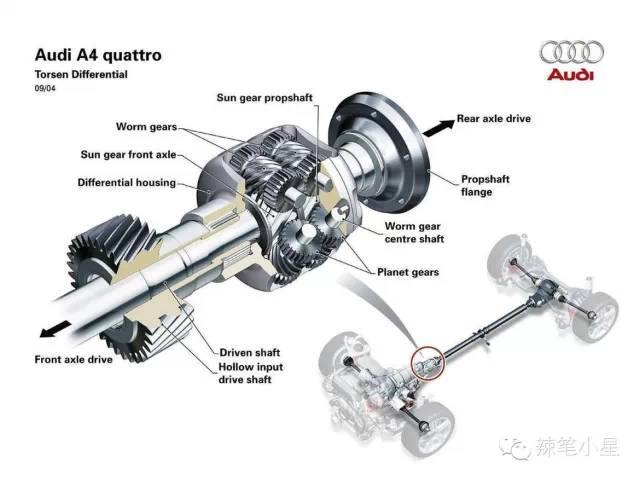
The development of Torsen torque induction transmission has made great progress so far. The full-time four-wheel drive system used by the Toyota Land Cruiser with the lowest configuration and Toyota’s domestically produced Prado 2.7L uses a Torsen torque-sensing transmission called Type C T3. Its structure is as follows. Compared with the original volume, it is smaller and more efficient.

On higher-priced Audi models, such as the Audi S4 or A6 Quattro, the latest sixth-generation Quattro system is used. Its core becomes a crown gear (Crown Gear) structure. Its characteristic is that it can transmit up to 85% of the torque to the rear axle (the front and rear axle torque distribution ranges from 15%/85% to 70%/30%). This has increased compared to the original adjustment range.

So what kind of mechanical solution is another viscous coupling differential?
This solution is to add a viscous silicone oil in the middle of the multi-plate clutch. The characteristic of this silicone oil is that when there is a large speed difference, the silicone oil will become more viscous as the temperature rises until it becomes almost solid. In this state, the wheel on the slipping side maintains the same speed as the wheel with friction. So this is also a simple mechanical solution that does not require electrical control. It mostly appears in the Subaru series of models, such as the Forester full-time four-wheel drive system (some models). Of course, the viscous coupling differential is not perfect, and its torque distribution needs to be realized by changing the name to silicone oil viscosity after the temperature is established by the speed difference, so there is a certain delay. Therefore, this type of differential is gradually being replaced by an electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential. For example, Subaru gradually replaced it with a compound planetary gear differential based on a central multi-plate clutch, which is the Subaru AWD system mentioned later.

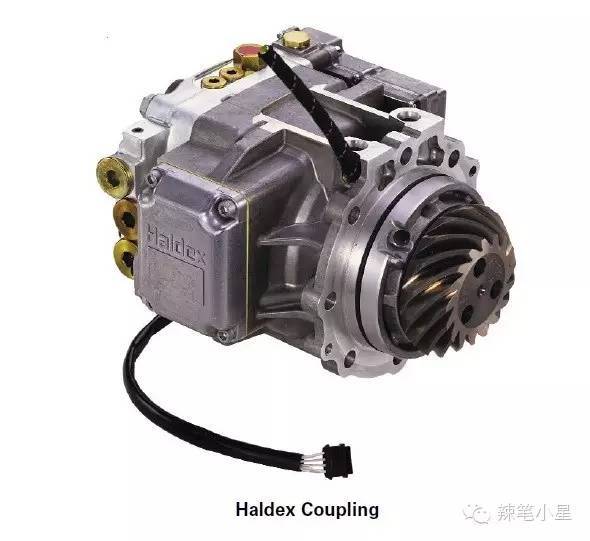
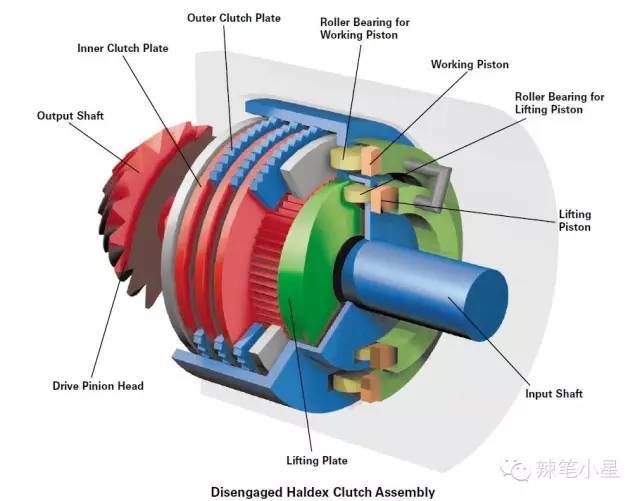
Let’s talk about the representative differential of the electronic school, that is, the multi-plate clutch differential. When it comes to multi-plate clutch differentials, I am afraid I have to mention a supplier, Haldex, Sweden. Because Hudson has helped many car companies realize the four-wheel drive system with its transverse four-cylinder engine. Among them, the 4Motion system with Volkswagen’s transverse engine is common, such as the timely four-wheel drive system of Volkswagen Tiguan, and the timely four-wheel drive models such as Land Rover Freelander 2 and Volvo XC60. Hudson’s electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential uses solenoid valves or electric motors to apply pressure to the multi-plate clutch, which sends torque to the rear axle. The torque delivered to the rear axle can be adjusted very flexibly. This allows torque distribution to be quickly adjusted to the driving dynamics. Its specific features include:
-
The four-wheel drive state is realized based on the electronically controlled multi-plate clutch
-
Can be flexibly switched to front drive
-
It responds quickly to changes in driving dynamics. such as quick start
-
Compatible with different tires, e.g. driving with a spare
-
There is no restriction on the grounding of the rear wheels when towing the vehicle, which will not damage the vehicle
-
Fully compatible with other electronic systems such as ABS, ESP or EDL.
-
Can only send up to 50% of the torque to the rear axle
-
Electronic-based systems are not as reliable as purely mechanical systems for harsh environments, such as possible overheating failures.
The following is the photo and structural diagram of the Hudson multi-disc clutch differential:

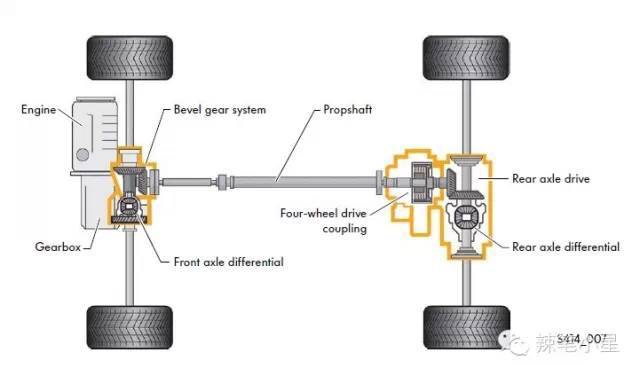
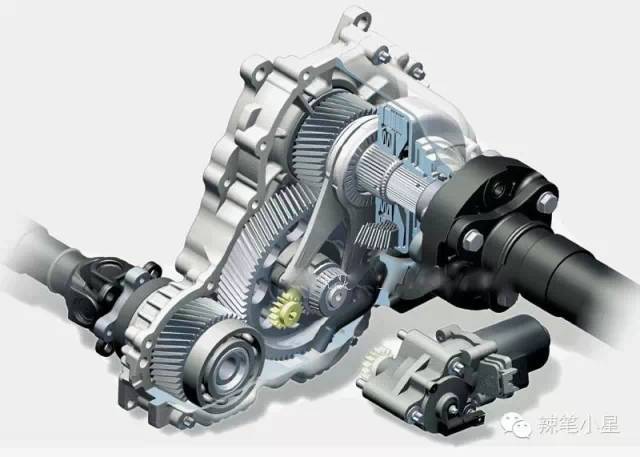
The following is the Volkswagen 4Motion system architecture based on the Hudson multi-plate clutch differential:
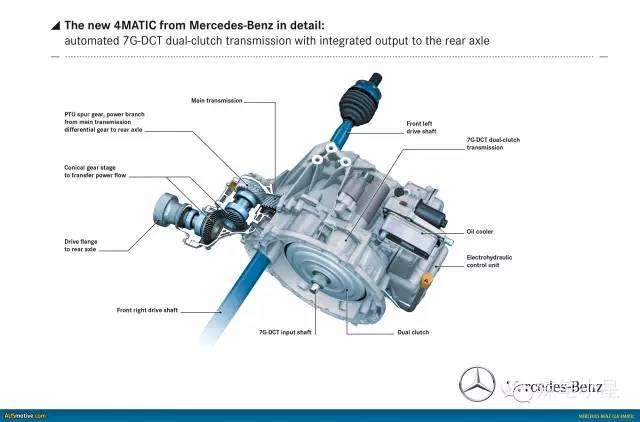
Of course, Hudson is not the only supplier that can provide multi-plate clutch differentials. For example, Mercedes-Benz has its own set of multi-plate clutch differential system called 4MATIC. They are respectively integrated in the 7G-DCT 7-speed dual-clutch transmission matched with the transverse engine and the 7G-Tronic 7G-Tronic automatic transmission matched with the longitudinal engine.
The electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential in the 7-speed dual-clutch gearbox of the Mercedes-Benz GLA four-wheel drive model is shown in the figure below. This set of multi-plate clutch differential can only transmit up to 50% of the torque to the rear axle, which is a timely four-wheel drive model. .
Different from the above, the electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential in the 7-speed automatic transmission of the Mercedes-Benz GLK four-wheel drive model can transmit nearly 100% of the torque to the front or rear axle. Its specific structure diagram is as follows. One of the planetary gear sets and the multi-plate clutch cooperate to realize the distribution of power between the front and rear axles, which belongs to the full-time four-wheel drive system.
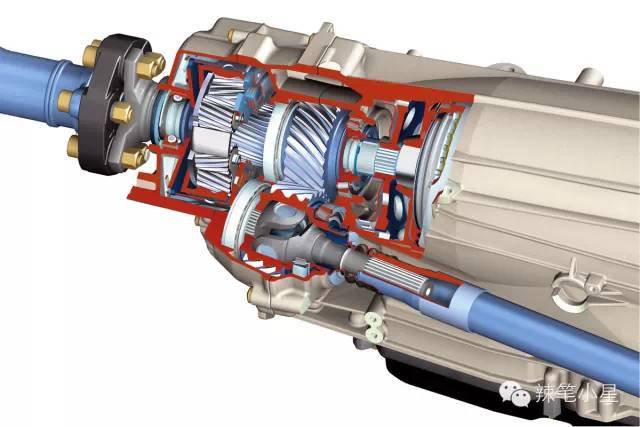
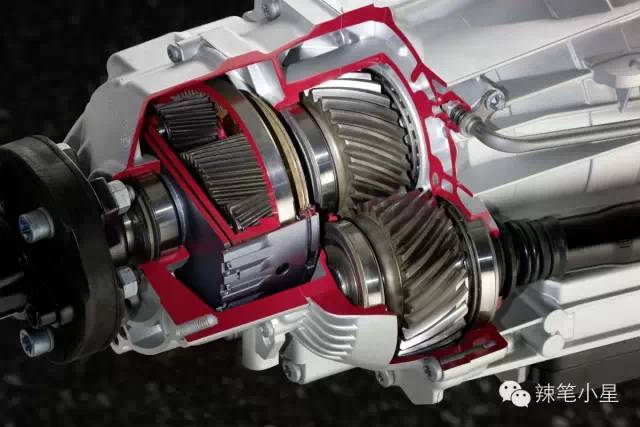
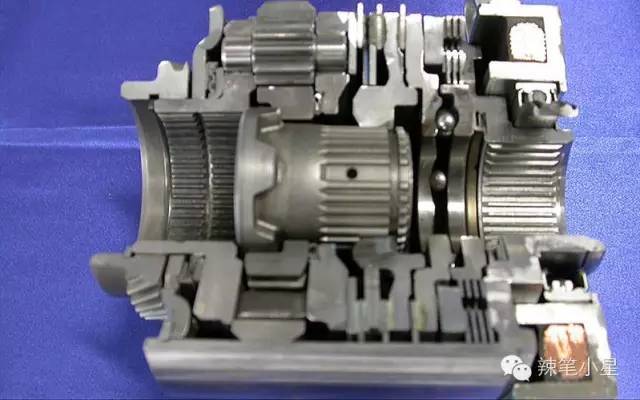
Similar to this, BMW also has an electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential integrated in its 8-speed automatic transmission, that is, the XDRIVE permanent four-wheel drive system. It can also send almost 100% of the torque to the front or rear axle. Its structure diagram is as follows. The system includes an electric motor that regulates the pressure sent to the multi-plate clutch to complete the distribution of torque between the front and rear axles. The system is used in BMW X1 and 3 Series XDRIVE models.

The aforementioned Subaru AWD system is also based on an electronically controlled multi-plate clutch differential, which is assembled on Subaru Outback models and Forester (some models). Subaru’s AWD system is called variable torque distribution AWD (Variable torque distribution AWD), or VTD for short. Based on a central multi-plate clutch compound planetary gear system. And the Subaru model also has a unique stunt, which we will list later.


So finished the mechanical school and electronic school of the central differential.
Let’s take a look at which models are equipped with the Rear Limited Slip Differential (LSD) on the rear axle.
In fact, many models on the market are not equipped with a rear axle limited slip differential. When the front wheels slip, the center differential distributes power to the rear wheels. What if one of the rear wheels also slips? Because there is a technology called Electronic Differential Lock (EDL). In fact, you can’t find any part called electronic differential lock in the car. Because it is just a function of an electronic stability system ESP. Its basic principle is to limit the rotation speed of the wheel on the slipping side by braking, so that the rotation speed of the wheel on the slipping side and the friction side is similar, and then transmit the torque to the wheel on the friction side through the ordinary differential. The premise of this is to detect that the wheel speed on the slipping side is too high, and then increase the braking force. This is the cheapest and easiest method to implement. It can be seen that no physical components have been added to the vehicle, but only a software upgrade for the braking system. But the electronic differential lock is not perfect. Now if you forget to release the handbrake when driving, sometimes you can drive with the first gear. When the wheels slip when the accelerator is high, it is not easy for the brake system to stop such a large power. And the time should not be too long, otherwise the brakes will overheat. Therefore, if you do not have high requirements for the off-road performance of the vehicle, then a model with an electronic differential lock is enough. If you want your car to be able to cope with more complex off-road conditions, it becomes necessary to choose a model with a rear axle limited slip differential.
The rear axle limited slip differential is also divided into mechanical type and electronic control type. For example, the lowest configuration of Toyota Land Cruiser, Toyota domestic Prado 2.7L, Land Rover Freelander 2 and Subaru Outback 3.6L (2.5L models are not equipped with rear axle limited slip differential) use mechanical rear axle limited slip differential. When one of the rear wheels slips, the rotation of the pinion in the rear axle limited-slip differential puts pressure on the low-speed, friction-side multi-plate clutch. At this time, the side with friction gets more torque. The specific structure diagram is as follows:
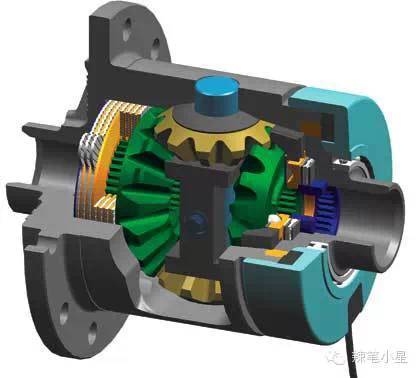
However, the electronically controlled rear axle limited-slip differential is mostly used in high-end cars, which is beyond the price range of the models we are mainly discussing today. Such as BMW X6 DPC (Dynamic Performance Control Dynamic Performance Control) differential and Audi A6 Quattro Sport Differential sports differential. This type of rear axle limited-slip differential is not only used for off-road, but more for better road handling performance. Therefore, it introduces a new concept called Torque Vector.
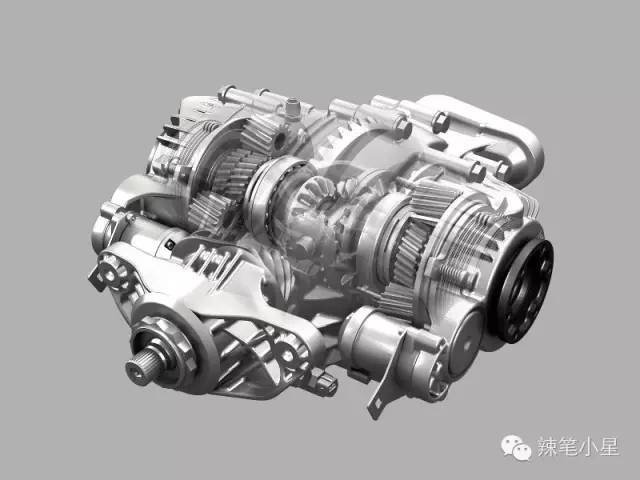
For example, BMW’s DPC rear axle differential has a set of electronically controlled multi-disc clutches on the left and right sides, and the degree of coupling of the multi-disc clutches can be adjusted by adjusting the hydraulic oil pressure on one side through the solenoid valve, so that the wheels on this side can get more power. Helps to steer the vehicle. The specific structure is as follows:


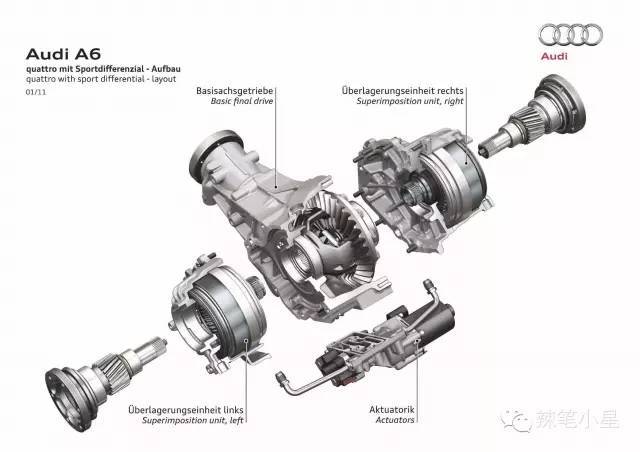
Audi’s Quattro Sport Differential sports differential also adjusts the torque of the left and right wheels based on a similar principle to realize the torque vectoring function, as shown in the following figure:
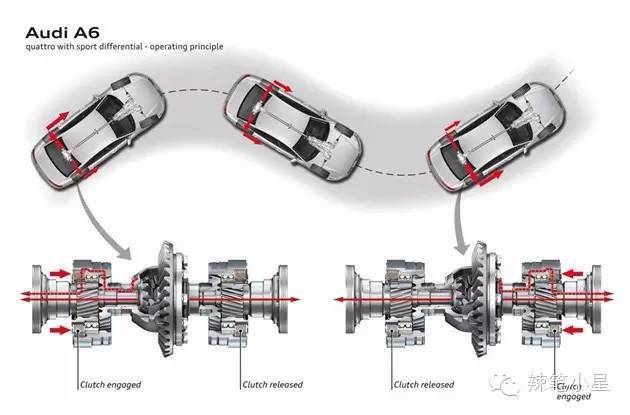
I believe everyone has also discovered that this type of electronically controlled rear axle differential has little to do with off-roading, and pays more attention to sports performance, and the cost is very high. So if you only pay attention to off-road performance, you can ignore the models equipped with this rear axle transmission.
Finally, I would like to talk to you about the aforementioned Subaru’s stunts. It is called a symmetrical four-wheel drive system (Symmetrical System).
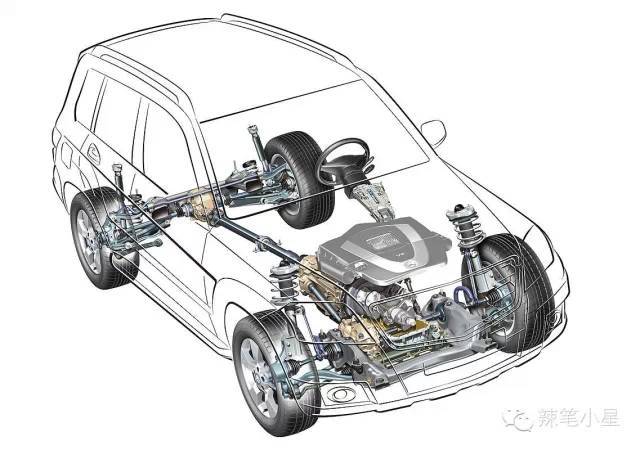
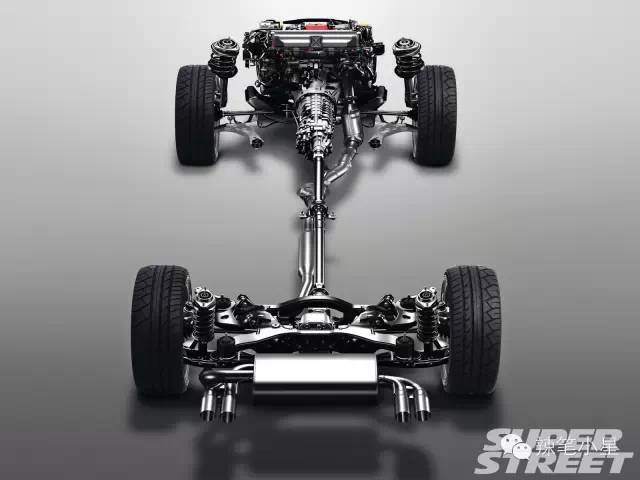
If you think carefully about the other car companies mentioned above, no matter the layout of the transverse engine or the longitudinal engine, it is impossible to put the differential in the center of the front axle. This is determined by the arrangement of the engine. The length of the transverse engine exceeds the central axis of the front axle. Although the longitudinal engine is arranged on the central axis of the front axle, but due to the length of the engine exceeds the front axle, it needs to be connected back to the front axle differential through the transfer device of the gearbox. At this time, the front axle differential can only be arranged on the side of the longitudinal engine. For details, please refer to the layout diagram of transverse engine and longitudinal engine in the figure below:
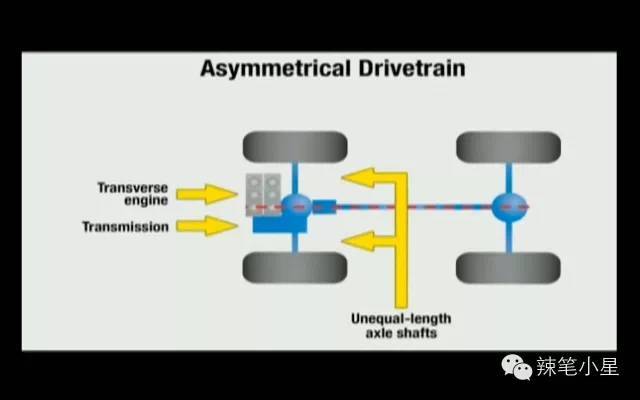

And the left-right length imbalance on the layout of the front axle differential will cause the differential to redistribute power when the front wheels slip and the vehicle will shake left and right. Subaru perfectly solved this problem. Because it is the only car company that insists on using horizontally opposed engines (in addition, Porsche still has horizontally opposed engine technology). In addition to being extremely well balanced, the boxer engine has the added benefit of being extremely short in length. It can be placed longitudinally on the central axis of the front axle, and then there is a suitable engine length to leave room for the differential. Therefore, Subaru’s four-wheel drive system is based on the left-right symmetry of the vehicle’s central axis. Then it avoids the problem of the vehicle shaking from side to side when the front wheels slip as mentioned above. The specific body layout and the comparison of symmetrical/asymmetrical systems can refer to the following figure:

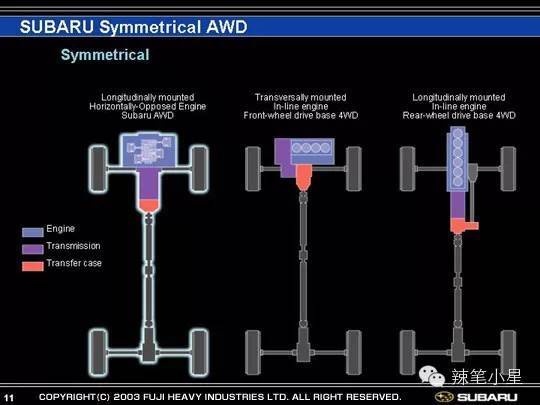
As mentioned before, when choosing a car, you must first pay attention to whether the central differential is a mechanical solution or an electronic solution. The mechanical solution is stable and reliable but the cost is high. The electronic solution is small and flexible but not stable enough to work for a long time. Regarding the rear axle limited-slip differential, if the off-road requirements are not high, you can choose a model that only uses electronic differential locks. If there are certain off-road requirements, it is recommended to choose a model equipped with a mechanical rear axle limited-slip differential. In addition, if you are interested in Subaru’s symmetrical four-wheel drive system, you can focus on it. Due to the left-right symmetry of its horizontally opposed engine layout, the problem of body shaking when skidding is solved.
Photo and text source: Spicy Pen Little Star