People’s requirements for tires are becoming more and more stringent. They not only hope that they can increase the friction between tires and the ground, but also hope that they can reduce tire noise and enhance comfort. The design and production of tires need to be considered in all aspects, not only to meet the needs of driving on dry and wet roads, but also on stone roads and mud roads.

The design of tires should take into account the climate characteristics of the four seasons, so that car owners do not have to change tires frequently. Before getting to know different types of tires, let’s start with the pattern.
1. Vertical pattern

The longitudinal pattern mainly plays the role of drainage, and the tire must be suitable for all road conditions, so wet and slippery roads are inevitable. The longitudinal pattern can effectively play a role in drainage, so that it is not easy to slip when the tire rotates and locks up. The grip is reduced, because the grain direction is usually parallel to the driving direction of the car, so the longitudinal pattern reduces the effective friction area between the tire and the ground, and too many longitudinal patterns will lead to insufficient grip of the tire.
2. Horizontal pattern
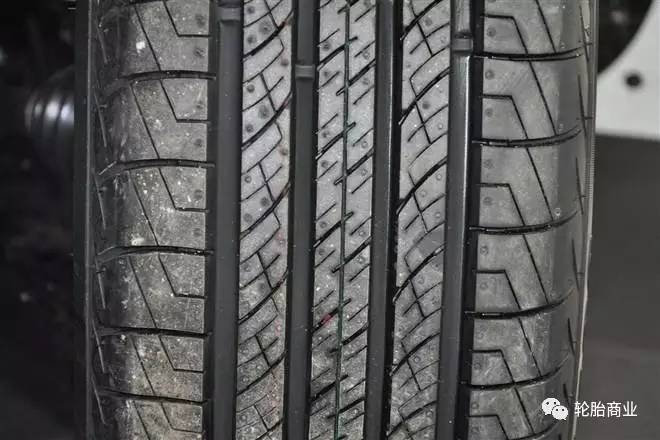

The transverse pattern has a higher grip ability, but the water drainage capacity under high-speed rotation is far less than that of the longitudinal pattern. The characteristics of the transverse pattern tire are just opposite to the longitudinal pattern.
3. Diagonal pattern
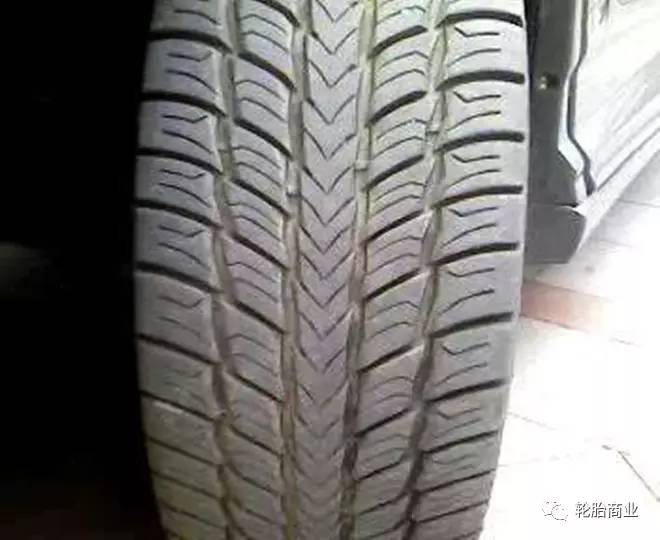

The patterns on most tires are not only densely distributed vertically and horizontally, but also intertwined with diagonal patterns. Its function is to break through the water film on the wet road and discharge it out of the tire. Don’t underestimate the water film. The tension of water can make tons of cars slip on the road.
So the design of the tire has become what it is today: the vertical pattern that provides fast drainage in the middle, the diagonal pattern and the transverse pattern that provides grip on the shoulders are combined into a perfect situation, so the mixed pattern is born. At present, this kind of mixed pattern tire is widely used in most vehicles such as cars, buses and trucks, and it is the most worry-free choice.
Asymmetric tread tire
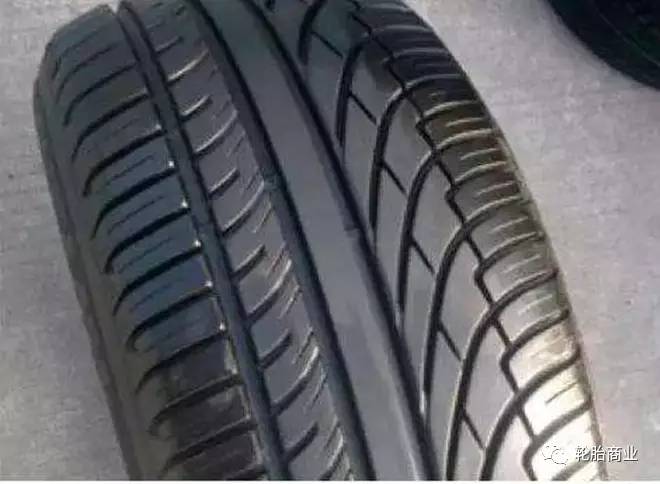

The left and right sides have different tread structures, and more attention was paid to the design of the design to increase the ground pressure of the outer treads when turning. This is why asymmetrical tires perform relatively well when cornering in certain situations. And taking into account the daily use, the wear resistance of the outer pattern of the asymmetric tire can also be improved accordingly.
Single-pipe tread tire
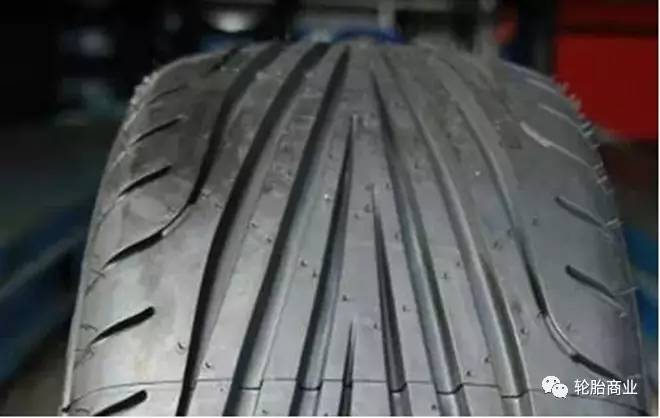

Single guide pattern tires have strong road performance and strong drainage capacity. The tires with this pattern will have relatively less rolling resistance towards a fixed rolling direction, and the vehicle handling will be better. Such a design makes it impossible for the single-guided tire to be reversed left and right, only the tires on the same side can be interchanged. Single guides have obvious arrows to indicate the rolling direction of the tire. Especially suitable for rainy or high-speed vehicles.
block tire
Block tires are generally used on off-road vehicles, and are mainly divided into three types according to different conditions of use: road tires, all-terrain tires and mud tires.
1) Road tires (HT tires)
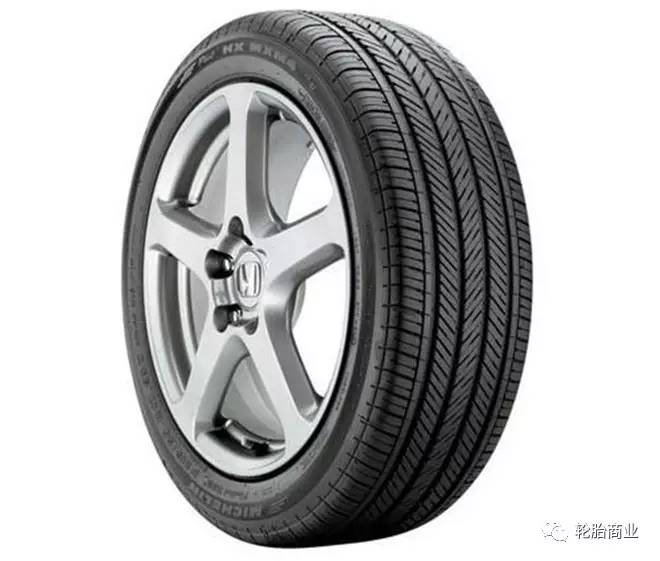

Road tires are referred to as HT tires. When off-road vehicles leave the factory, new vehicles are usually installed with neutral road pattern tires, which are mainly used for road driving, and are characterized by relatively soft tire walls and fine tread patterns.
2) All Terrain Tires (AT Tires)
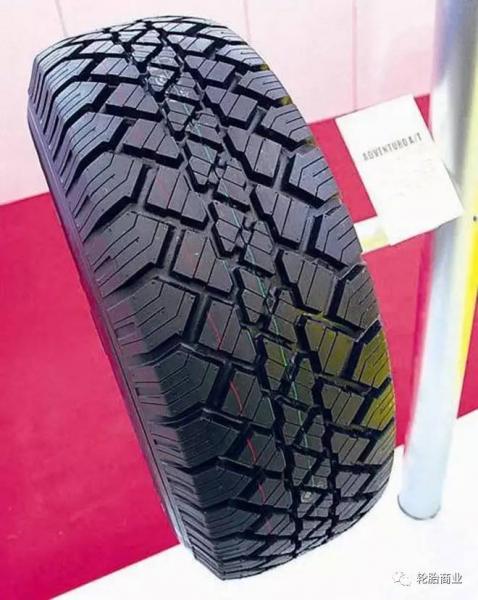

The design of all-terrain tires is more compatible than that of road tires. The pattern design of all-terrain tires is relatively rough, and the spacing between tire teeth is slightly larger than that of road tires. The negative effect of this design is that the road performance is reduced and the noise is increased, but the durability and adhesion on non-paved roads are stronger than road tires. It is a tire with both off-road and road performance.
3) Mud Terrain Tires (MT Tires)
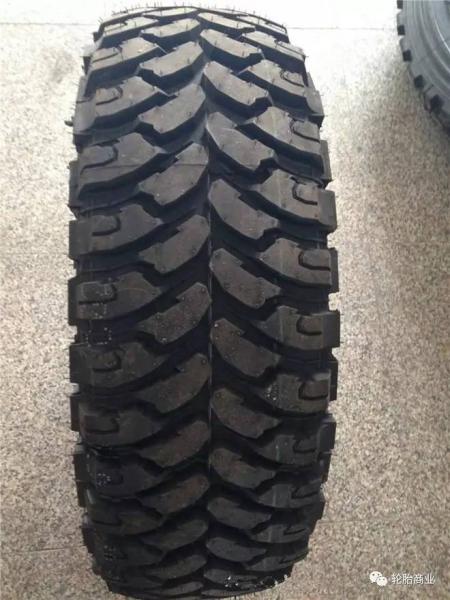

Mud-terrain tires are the opposite of road (HT) tires. MT tires have hard walls, exaggerated tire teeth, and the distance between the tire teeth is significantly larger. It is convenient to discharge mud at a slow speed or throw mud at a high speed when driving on muddy ground, and it is easier to increase adhesion on some harsh ground, such as uneven rocky ground. When driving on the road, the noise of MT tires is very loud. When the vehicle speed is lower than 10km/h, the vibration of the tire teeth will be felt. If driving on a rainy paved road, it is easier to lose control.
Source of pictures and texts: Tire Business Network.